The Rise of Cybersecurity Challenges in 2025: The Growing Threat of Phishing and Cybercrime
 2025.10.12 12:49
2025.10.12 12:49As we venture deeper into the digital age, where everything from our social lives to business operations is intricately linked to the internet, the threat of cybercrime continues to loom large. With businesses, governments, and individuals relying heavily on digital tools and platforms, the sophistication and scale of cyber threats have escalated in alarming ways. Among these threats, phishing attacks have become one of the most prevalent and damaging forms of cybercrime.
Phishing is no longer a simple scam—it has evolved into a highly sophisticated weapon used by cybercriminals to target unsuspecting victims and exploit their vulnerabilities. This article explores the rise of phishing attacks, the threat they pose in 2025, and the best ways to combat these malicious activities.
What is Phishing?
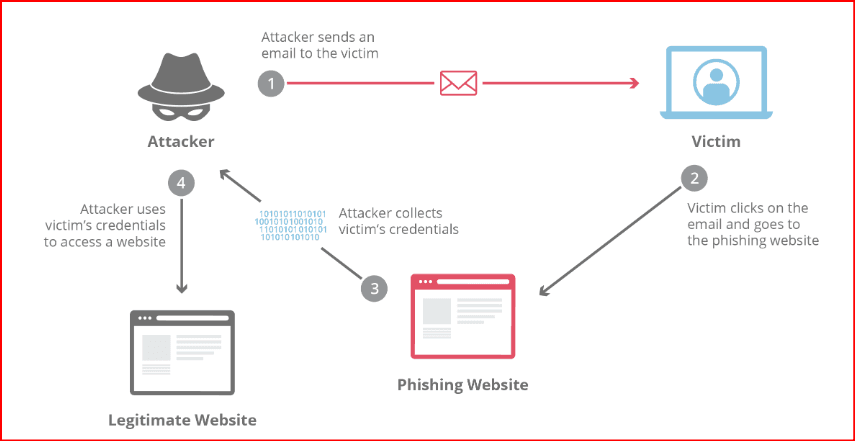
Phishing is a form of cybercrime where attackers deceive individuals into revealing sensitive information such as login credentials, financial details, or personal identification. This information is then used for malicious purposes, including identity theft, unauthorized transactions, and sometimes, blackmail. Attackers rely heavily on social engineering tactics, exploiting human vulnerabilities such as trust, curiosity, and fear.
In 2025, phishing attacks are expected to be even more dangerous due to their advanced nature and the increasing reliance on digital communication. With the advent of AI-powered phishing techniques and more integrated communication channels like voice, video, and social media, identifying a phishing attempt will become increasingly difficult.
Types of Phishing Attacks in 2025
In 2025, phishing will continue to evolve, with new strategies being devised every year. Here are some of the most common forms of phishing attacks to be aware of:
Email Phishing
While this remains the most common form of phishing, email phishing has grown much more sophisticated. Attackers now employ AI and machine learning to tailor phishing emails that look increasingly legitimate. They mimic emails from reputable organizations, often spoofing their logos, signatures, and web links to trick recipients into clicking on malicious links or downloading infected attachments.
Example in 2025: A phishing email may look like a notification from a legitimate financial institution about a critical update or security alert. Clicking the link, however, leads to a fraudulent login page designed to capture your login credentials.
Spear Phishing
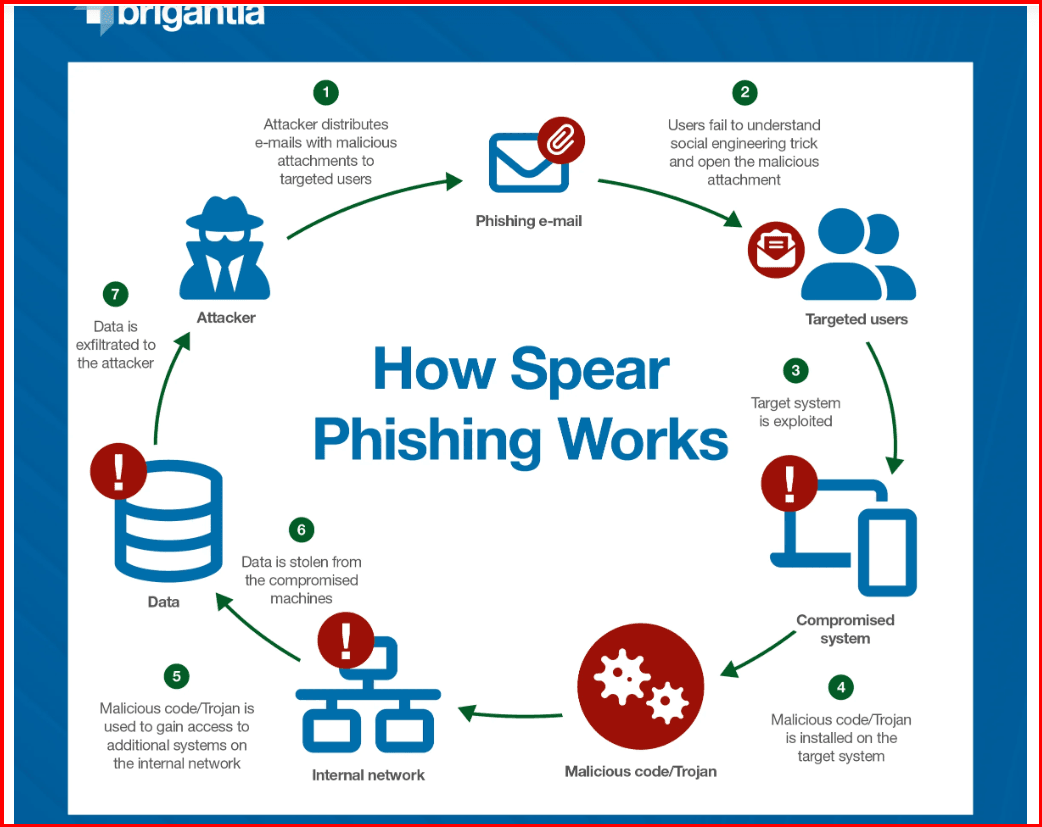
Unlike mass phishing attacks, spear phishing is highly targeted. Attackers spend time researching their victims—whether they're individuals or high-profile employees in a company—and craft personalized emails that increase the likelihood of success.Example in 2025: An executive at a major corporation receives an email disguised as a request from a colleague or business partner. The email might request sensitive company information or ask for urgent wire transfers to an external bank account.
Whaling (CEO Fraud)
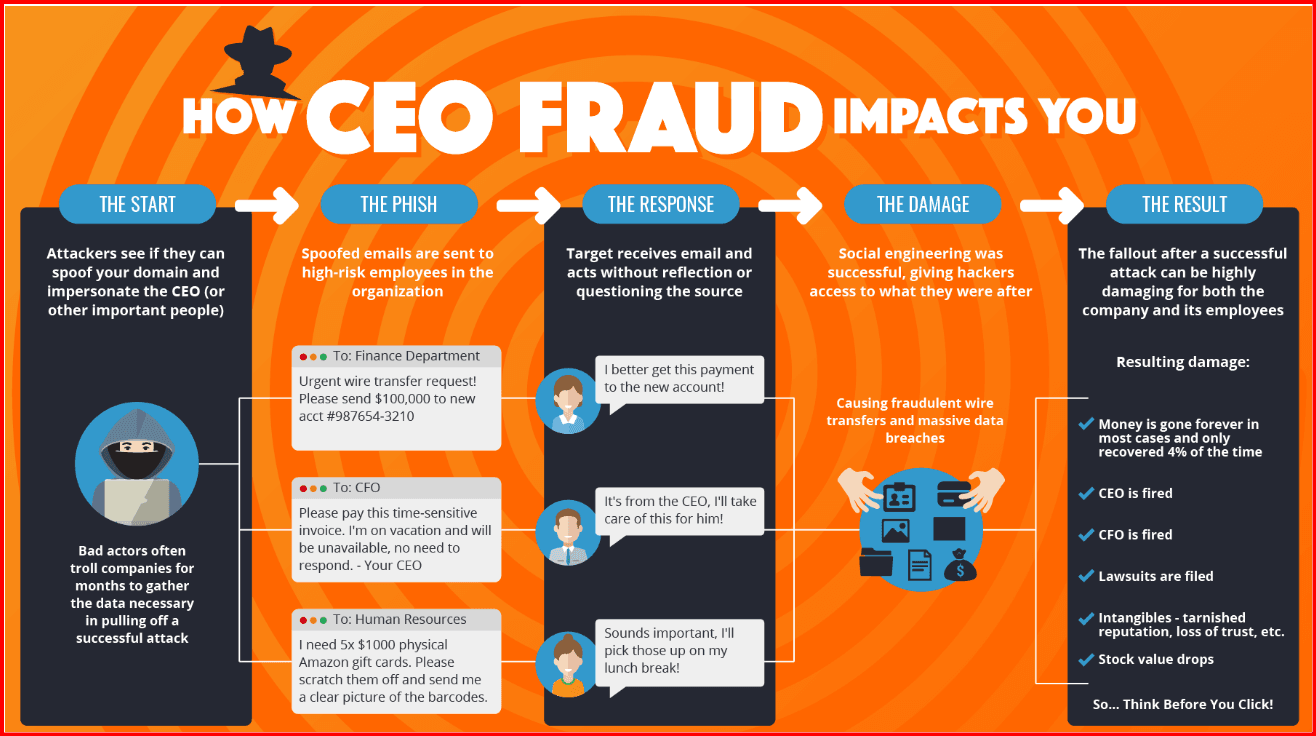
Whaling is a form of spear phishing, but it targets high-level executives, such as CEOs, CFOs, or board members. These attacks often lead to significant financial losses since they exploit the trust and authority of top executives.Example in 2025: A cybercriminal impersonates a CEO, sending an urgent message to the company's financial officer requesting the immediate transfer of a large sum of money to a "new account."
Voice Phishing (Vishing)
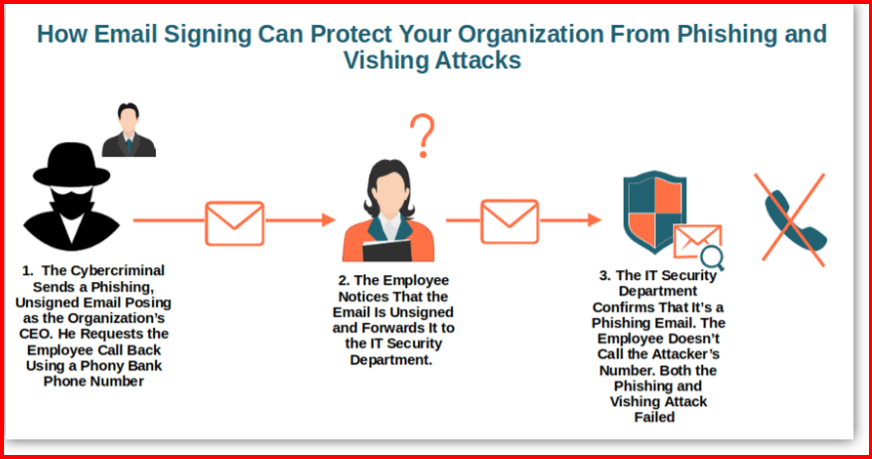
As voice technology improves and becomes more integrated with digital assistants, vishing attacks have grown more convincing. Attackers spoof phone numbers to impersonate legitimate institutions, such as your bank, and attempt to extract sensitive information via phone calls.Example in 2025: You receive a call from what seems like your bank’s official phone number, claiming that there is suspicious activity on your account. The attacker urges you to verify your account details over the phone.
SMS Phishing (Smishing)
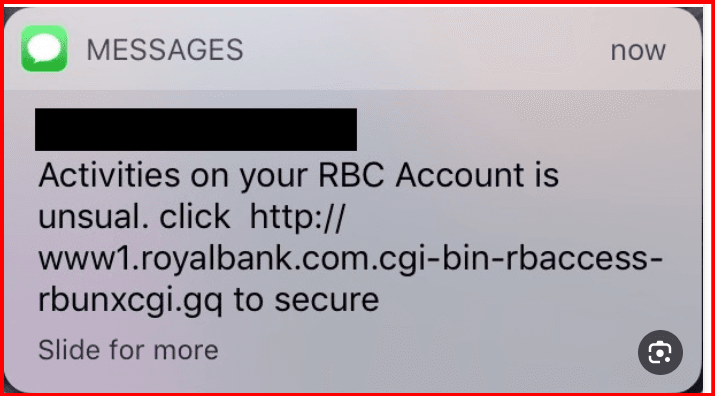
SMS phishing continues to be a widespread attack vector. In 2025, smishing attacks are predicted to become even more sophisticated, utilizing AI to generate highly personalized messages. These messages often contain links to fake websites designed to steal sensitive information.Example in 2025: A text message claims that you've won a prize and directs you to a website to claim it. The website is designed to steal your payment details or install malware on your device.
Social Media Phishing (Soshing)
Phishers are increasingly using social media platforms to engage potential victims. In 2025, attackers may impersonate friends, colleagues, or popular public figures on platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram to gain access to private information or spread malicious links.Example in 2025: A direct message on Twitter appears to be from a trusted contact, asking you to click on a link to a supposedly urgent document. The link leads to a site that steals your login credentials or installs malware.
Search Engine Phishing
This attack type involves creating fraudulent websites that mimic popular online stores or services. These fake sites are designed to appear in search engine results, tricking victims into visiting them.Example in 2025: A search for a popular e-commerce website leads you to a site that offers unbeatable deals. After entering your credit card information, your payment details are stolen.
Pharming
Pharming is a more advanced form of phishing where cybercriminals manipulate DNS settings to redirect users to fake websites. Unlike other types of phishing, pharming doesn’t require users to click on a malicious link—users are redirected automatically to fraudulent sites when they type in a legitimate URL.Example in 2025: You try to access your bank’s website, but you are redirected to a fraudulent site that looks identical. Your login credentials are then stolen.
How Will Phishing Evolve in 2025?
In 2025, phishing attacks are expected to become more sophisticated, aided by AI, machine learning, and deeper social engineering tactics. These advancements will make it harder for individuals to distinguish between legitimate and malicious communications. Additionally, as we see an increase in the adoption of voice assistants, smart devices, and automated services, phishing attacks could exploit these technologies to deceive even the most tech-savvy individuals.
Here are a few developments to expect:
- AI-Generated Phishing Campaigns: Artificial intelligence will enable attackers to craft highly convincing phishing emails and messages that are tailored to individual victims. These emails will use information harvested from social media and other online platforms to increase their credibility.
- Deepfake Technology: With the rise of deepfake technology, attackers could impersonate voices or even video calls from trusted contacts. A deepfake phone call, for instance, could trick an employee into transferring funds to a fraudster.
- Automation in Phishing: Automated systems powered by AI could launch large-scale phishing campaigns without the need for human intervention. These systems could analyze potential victims' online activity to personalize their phishing messages.
- More Advanced Malicious Websites: As attackers become more adept at mimicking legitimate websites, it will be harder to tell the difference between real and fake sites. In 2025, advanced techniques such as browser-injected phishing will become more common, where the malicious code is injected directly into a legitimate site.
How Can You Protect Yourself in 2025?
As phishing attacks become more sophisticated, it’s essential to adopt advanced security measures to protect yourself and your organization. Here are some tips:
- Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Enabling MFA is one of the most effective ways to add an extra layer of security to your accounts, making it harder for attackers to gain access even if they have your password.
- Be Skeptical of Unsolicited Messages: Whether it’s an email, text, or voice call, always verify the source of any communication that asks for sensitive information. Don’t click on links or download attachments from unknown sources.
- Educate Yourself and Others: Continuous cybersecurity training is crucial in staying ahead of phishing tactics. Organizations should offer regular training sessions for employees to help them recognize phishing attempts.
- Implement Strong Email Filters: Utilize advanced email filtering systems to detect phishing emails before they reach your inbox. These filters can help prevent malicious attachments or links from causing harm.
- Regularly Monitor Accounts and Financial Statements: Regularly reviewing your financial statements, credit reports, and online accounts can help detect suspicious activity early.
- Keep Your Software Up to Date: Ensure your devices and applications are updated with the latest security patches. Attackers often exploit known vulnerabilities in outdated software.
Conclusion
As we look towards 2025, phishing attacks will only grow more complex and pervasive. However, by staying informed and adopting a proactive approach to cybersecurity, individuals and organizations can significantly reduce their chances of falling victim to these malicious schemes. The key to staying safe in this digital age is vigilance—recognizing threats, verifying sources, and always erring on the side of caution.
 petro
petro
 Multi-Account Management
Multi-Account Management Prevent Account Association
Prevent Account Association Multi-Employee Management
Multi-Employee Management