What is Browser Leak? How to Test and Prevent It with Whoer and BitBrowser
 2025.11.12 03:51
2025.11.12 03:51Your browser may be exposing more information than you expect. Even when you use a VPN or browse in incognito mode, websites can still identify your real IP address, system settings, and unique fingerprint. These hidden exposures are known as browser leaks and they allow platforms to track your activity or link multiple accounts to the same device.
This guide explains what a browser leak is, how it occurs, and how tools such as Whoer help you detect it. You will also learn how privacy solutions like BitBrowser strengthen your protection by creating controlled and isolated browsing environments. Understanding browser leaks is the first step toward safeguarding your online identity.
What is Browser Leak?
Browser leaks occur when your web browser unintentionally exposes identifying information about your device and browsing habits, even when you're using privacy tools like VPNs or browsing in incognito mode. You might believe these tools safeguard your identity, but they often fail against advanced tracking techniques.
1. How does a browser leak happen?
Your browser continually transmits data to websites you visit. This process, known as browser fingerprinting, gathers an astonishing amount of information:
· Device characteristics: Screen resolution, operating system, hardware specifications
· IP address: Your actual location data (sometimes bypassing VPN protection)
· System language: Default language and timezone settings
· Installed plugins: Browser extensions, fonts, and add-ons
· WebRTC data: Real-time communication protocols that can disclose your true IP address
2. The role of WebRTC in browser leaks
WebRTC deserves special attention here. This technology enables direct connections for video calls and file sharing, but it can bypass your VPN entirely, exposing your genuine IP address to any website that queries it.
3. Why is browser leak a concern?
The consequences of browser leaks go beyond mere tracking. When websites gather your browser fingerprint, they construct a unique profile that follows you across the internet. This profile remains unchanged even when you:
1. Switch to incognito mode
2. Clear your cookies
3. Use different accounts on the same platform
For anyone managing multiple online accounts—whether for business, e-commerce, or social media—browser leaks present significant operational risks. Platforms can identify that seemingly separate accounts originate from the same device, potentially causing account suspensions or bans.
The tracking doesn't end with inconvenience. Exposed data feeds into targeted advertising networks, creating detailed profiles of your interests, habits, and online behavior. In extreme cases, persistent tracking can result in identity exposure, linking your anonymous browsing activities back to your real-world identity.
Core Risk: Unlike an IP address, which can be shared or changed, a comprehensive browser fingerprint is often unique and persistent, making it a powerful tool for platform risk control systems to identify and track users.
Understanding browser leaks is your first step toward reclaiming online privacy in an increasingly monitored digital world.
Whoer: A Tool for Testing Browser Leaks
Whoer stands out as one of the most accessible and comprehensive online tools for conducting a browser leak test. You can access it directly through your web browser without installing any software, making it an ideal first step in assessing your privacy vulnerabilities. The platform has gained popularity among privacy-conscious users, security professionals, and anyone managing multiple online accounts.
1. How Whoer Works
How Whoer works is straightforward: the moment you visit the website, it automatically begins scanning your browser and connection to detect potential leaks. The tool performs real-time analysis and presents results in an easy-to-understand format, assigning an overall anonymity score that indicates how well your browser protects your identity.
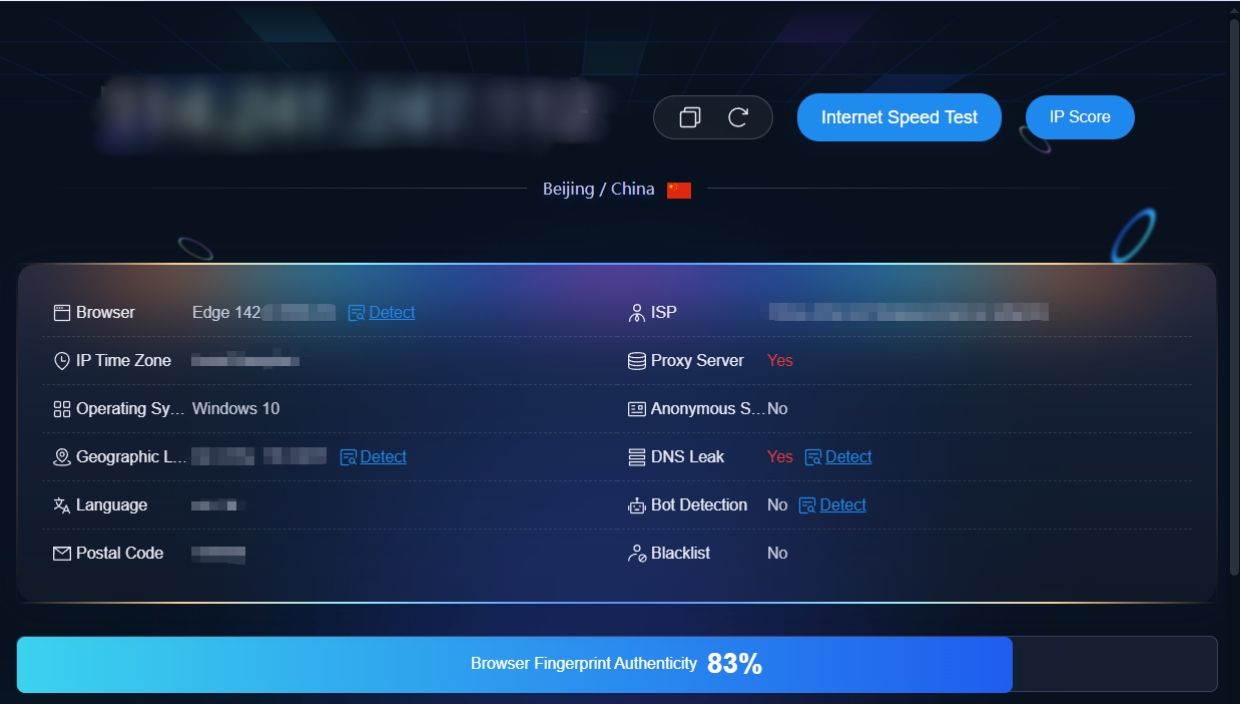
2. What Whoer Analyzes
The types of data Whoer analyzes include:
· IP address information: Your real IP address, location data, and whether you're using a proxy or VPN
· DNS requests: Whether your DNS queries leak outside your VPN tunnel, revealing your actual ISP
· WebRTC leaks: Detection of your local and public IP addresses through WebRTC connections
· Browser fingerprint elements: Screen resolution, installed fonts, timezone, system language, and browser plugins. This aspect is crucial as it relates to browser fingerprinting, a technique that can be used to track users across the web.
· HTTP headers: User-agent strings and other technical identifiers your browser sends with each request
You'll receive detailed breakdowns of each category, with color-coded indicators showing which elements pose privacy risks and which remain protected.
Step-by-Step Guide: Using Whoer to Test for Browser Leaks
Running a browser leak test with Whoer takes just seconds. Navigate to whoer.net and the tool automatically begins analyzing your connection. You don't need to click anything—the scan starts immediately upon page load.
1. How to Test Browser Fingerprint with Whoer
The Whoer interface displays your results in real-time:
1. Check your anonymity score at the top of the page (displayed as a percentage)
2. Scroll down the page to view detailed results for each test item. Pay close attention to these high-risk areas:
· Canvas fingerprint status
· WebGL renderer information
· WebRTC IP address leak
· Number of fonts listed
3. Expand detailed sections by clicking on specific categories like "WebRTC," "DNS," or "Geolocation"
4. Compare your visible IP against your actual location to verify VPN effectiveness
2. Interpreting Your Test Results
A score below 80% typically indicates significant privacy vulnerabilities. Pay special attention to WebRTC leaks, which can expose your real IP address even when connected to a VPN. DNS leaks reveal which servers handle your browsing requests, potentially linking your activity to your ISP.
If your Whoer test results remain consistent after multiple page refreshes, it indicates a stable browser fingerprint, making long-term tracking easier.
Red flags in your Whoer report demand immediate attention. If your system language, timezone, or screen resolution create a unique fingerprint combination, websites can track you across sessions. The "Do Not Track" setting paradoxically makes you more identifiable when enabled, as fewer users activate this feature.
3. Browser Leak Test Tools Beyond Whoer
While Whoer is a powerful tool, it's beneficial to explore other options for comprehensive testing. You might want to consider some of the best browser checking tools available that provide different perspectives on potential vulnerabilities:
· BrowserLeaks provides comprehensive fingerprinting analysis, including IP address, WebRTC, Canvas, WebGL, fonts, media devices, and more. It is suitable for in-depth analysis of specific types of leaks.
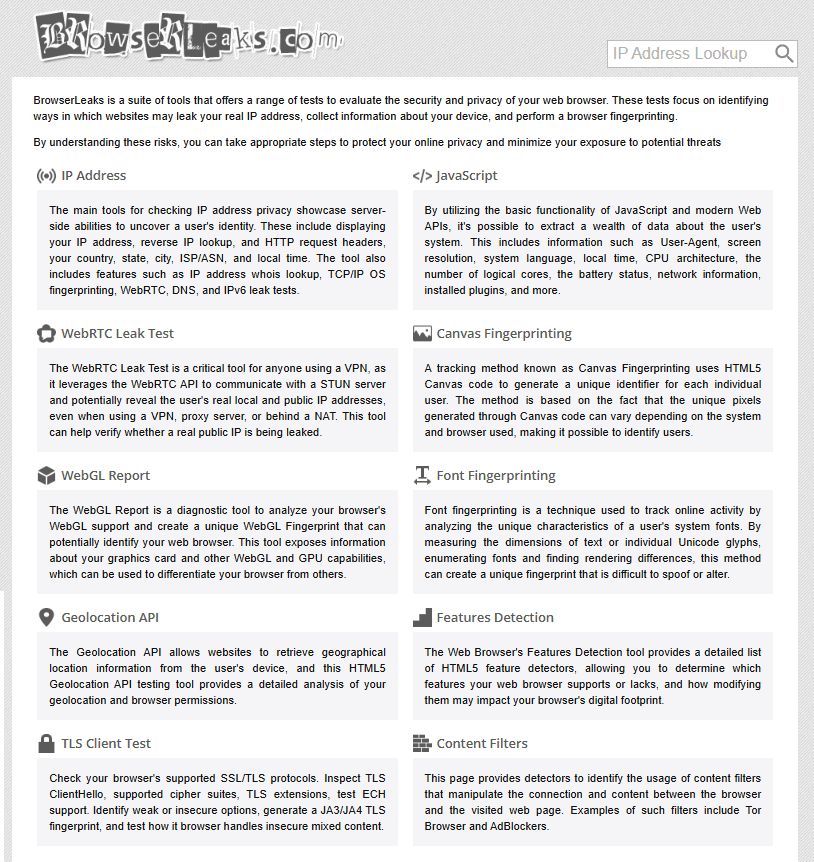
· IPLeak (ipleak.com) specializes in detecting IP address, DNS, and WebRTC leaks, making it ideal for verifying whether VPNs or proxies are functioning properly.
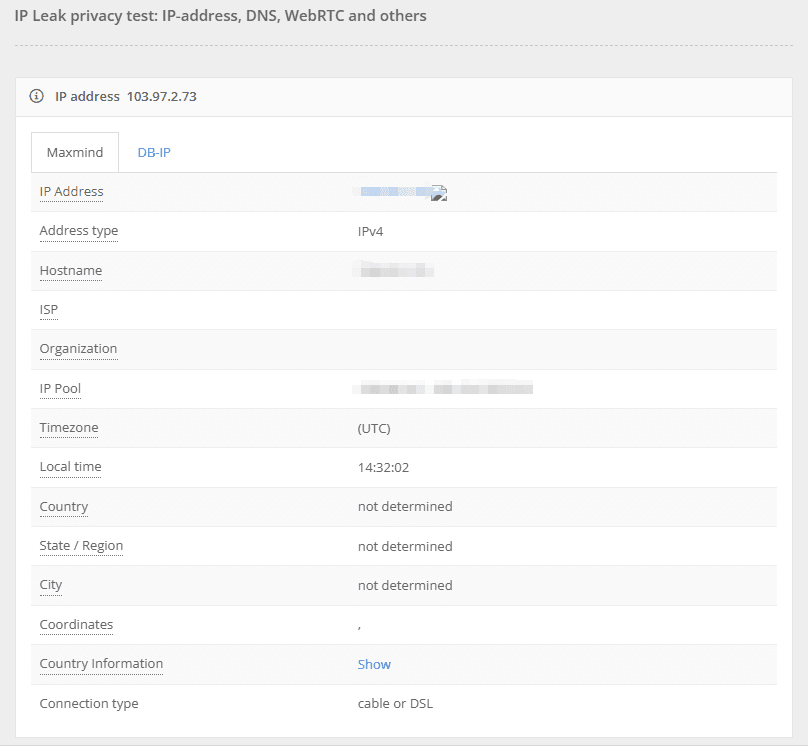
· IPhey (iphey.com) can be used to validate the effectiveness of anti-fingerprinting browser extensions or configurations by checking for risks such as IP address leaks, WebRTC leaks, or DNS leaks.
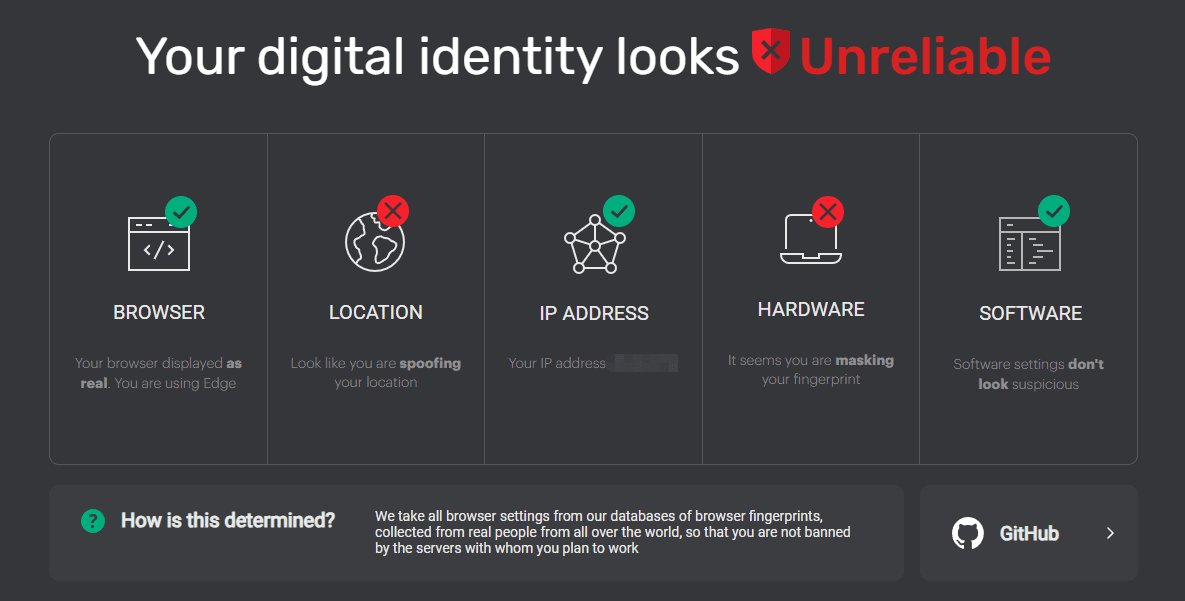
Running tests across multiple platforms gives you a complete picture of your browser's privacy posture.
Best Practices for Preventing Browser Leaks
Testing for browser leaks is just the first step—you need to actively implement prevention strategies to protect your digital identity. The techniques below will help you prevent browser leak issues and prevent online tracking across your browsing sessions.
1. Regularly Conduct Browser Leak Tests
You should check your browser for leaks at least once a month using tools like Whoer. Your browser configuration changes over time through updates, new extensions, and modified settings. Each change potentially introduces new vulnerabilities.
Set a recurring reminder to run leak tests, especially after:
· Installing new browser extensions or plugins
· Updating your operating system or browser
· Changing VPN providers or network configurations
· Adding new hardware devices to your system
2. Leverage Built-in Browser Privacy Features
Modern browsers offer basic anti-fingerprinting protections:
· Firefox: Enable privacy.resistFingerprinting in about:config.
· Brave: Comes with strong anti-fingerprinting protection enabled by default.
· Safari: Activate "Prevent cross-site tracking" and "Privacy Preserving Ad Click" features.
· Chrome and Edge users need to install extensions like WebRTC Protect - Protect IP Leak or uBlock Origin with WebRTC blocking enabled.
3. Lock Down Location and Media Access
Your browser constantly requests access to location services, cameras, and microphones. These permissions create additional tracking vectors. Navigate to your browser's privacy settings and:
· Block location access for all websites by default
· Disable automatic camera and microphone permissions
· Review and revoke permissions for sites you've previously granted access to
· Enable "ask before accessing" for all media devices
4. Deploy Privacy-Focused Extensions
Strategic extension choices significantly reduce your leak surface area. Install these essential tools:
· uBlock Origin: Blocks tracking scripts and ads that collect fingerprint data
· Privacy Badger: Learns and blocks invisible trackers automatically
· Canvas Blocker: Prevents canvas fingerprinting techniques

· Cookie AutoDelete: Removes tracking cookies when you close tabs
Note: Avoid installing too many extensions—each one modifies your browser fingerprint and makes you more identifiable.
5. Isolate Your Browsing Activities
Sandboxed environments and virtual machines create complete separation between your browsing sessions. Tools like Sandboxie or Windows Sandbox let you run your browser in an isolated environment. When you close the sandbox, all browsing data disappears completely.
Virtual machines take this concept further by running an entire operating system in isolation. You can create different VM profiles for various online activities, ensuring your browsing patterns never overlap.
Advanced Prevention Tools: Anti-Detect Browsers and BitBrowser
Standard browsers weren't designed with fingerprint protection as a priority. Anti-detect browsers solve this problem by giving you complete control over your digital fingerprint. These specialized tools let you customize every aspect of your browser's identity—from canvas fingerprints to WebGL parameters.
BitBrowser takes fingerprint customization to the next level. The platform allows you to create multiple browser profiles, each with unique fingerprint configurations. You can modify device characteristics, timezone settings, language preferences, and hardware specifications for each profile. This approach helps you prevent browser leak vulnerabilities while maintaining separate online identities for different purposes.
BitBrowser helps prevent browser leaks through several mechanisms:
· Fingerprint Customization: Allows full customization of browser fingerprint parameters, including advanced features like Canvas, WebGL, and fonts.
· Environment Isolation: Creates completely isolated browsing profiles for each session, preventing cross-session tracking.
· Fingerprint Consistency: Ensures all fingerprint parameters are coordinated and realistic, avoiding detection as a synthetic browser.
· Batch Management: Supports managing multiple independent browser profiles simultaneously, each with a unique digital fingerprint.
Please refer to our article to learn how to protect your online anonymity and privacy using Whoer and BitBrowser.
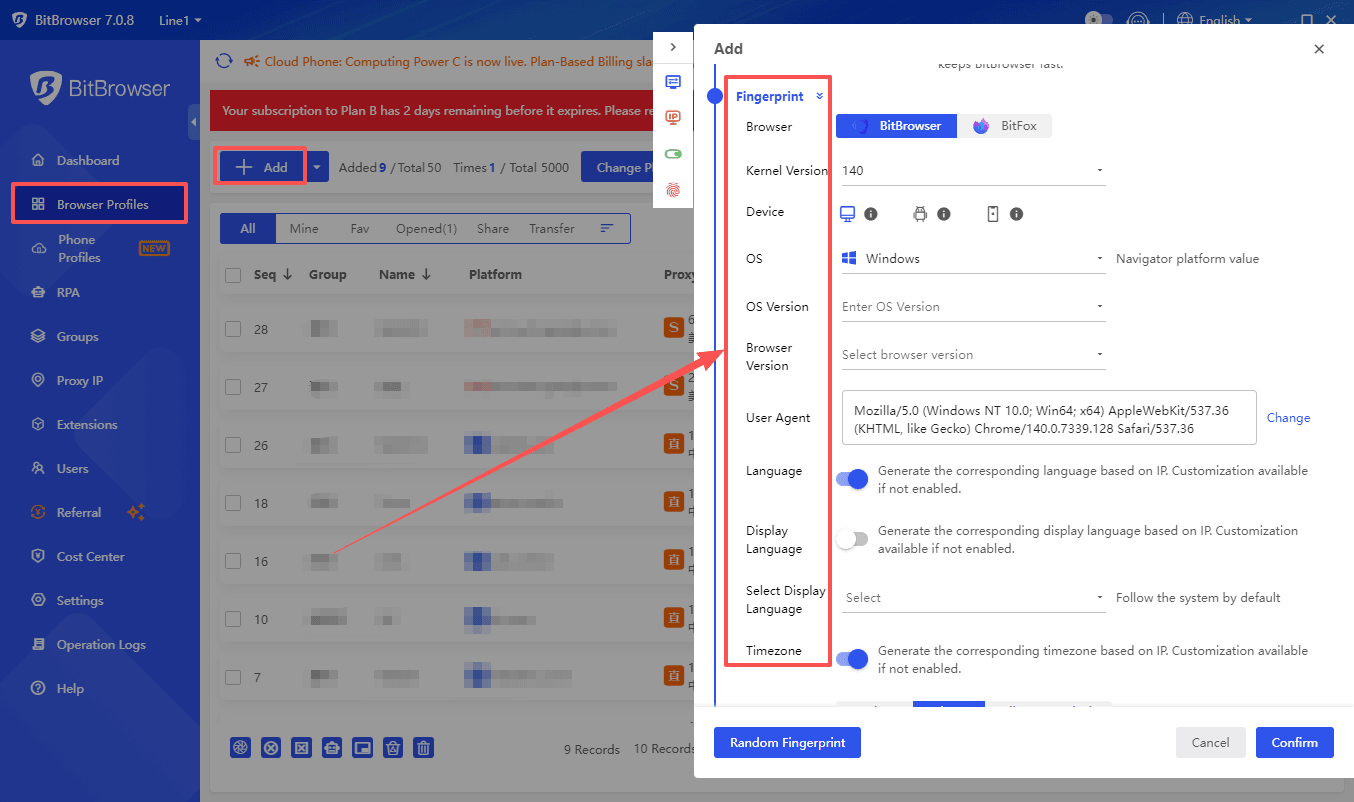
The anti-detect browser generates consistent, believable fingerprints that websites recognize as legitimate. You're not just blocking tracking—you're presenting controlled, authentic-looking browser characteristics.
Learn more about BitBrowser's fingerprint customization features to understand how custom profiles protect your privacy without triggering anti-fraud systems.
Conclusion
Your browser reveals more about you than you might think. What is Browser Leak? Run a test on Whoer right now to see what information you're exposing. The results might surprise you.
Protecting your digital footprint requires actionable privacy tips you can implement immediately: disable WebRTC, use anti-detect browsers like BitBrowser for multi-account management, and make leak testing part of your secure browsing habits. These aren't optional steps—they're essential defenses against tracking, fingerprinting, and identity exposure.
FAQ
1. What is a browser leak and why does it matter?
A browser leak occurs when your browser exposes identifiable data—such as IP address, timezone, fonts, and WebRTC information—to websites without your consent. This matters because the exposed data forms a persistent browser fingerprint that can track you across websites, link multiple accounts to one device, and undermine VPN or incognito mode protection.
2. Can WebRTC leak my real IP address even when I'm using a VPN?
Yes. WebRTC can establish peer-to-peer connections that completely bypass your VPN tunnel. Even with a VPN active, websites can still detect your real IP address unless WebRTC is blocked or restricted through browser settings or extensions. This is one of the most common and dangerous browser leaks.
3. How does Whoer help detect browser leaks?
Whoer automatically scans your browser for major leak vectors, including IP address information, DNS requests, WebRTC exposure, fingerprinting elements, HTTP headers, and more. It also provides an anonymity score that summarizes your overall privacy level. This makes it one of the simplest ways to quickly check your browser’s security posture.
4. What should I do if my Whoer test shows a low anonymity score?
A low score (below 80%) means your browser has multiple leak points. Start by blocking WebRTC, enabling anti-fingerprinting protections, reviewing DNS settings, revoking camera/microphone permissions, and removing unnecessary extensions. For advanced privacy needs—especially multi-account work—using an anti-detect browser such as BitBrowser offers far stronger protection and fingerprint control.
5. How can BitBrowser help prevent browser leaks more effectively than regular browsers?
BitBrowser allows you to fully customize and isolate browser fingerprints. Each profile can have its own device parameters, timezone, language, WebGL/Canvas settings, and hardware identifiers. This prevents fingerprint-based tracking, ensures profiles do not overlap, and avoids platform risk-control systems detecting multiple accounts from the same device. It's an essential tool for professionals who need reliable multi-account privacy.
 YT.Shi
YT.Shi
 Multi-Account Management
Multi-Account Management Prevent Account Association
Prevent Account Association Multi-Employee Management
Multi-Employee Management