What Is an Anti-detect Browser? Complete Guide for Beginners
 2025.12.09 06:09
2025.12.09 06:09In 2025, digital marketers, e-commerce entrepreneurs, and privacy-conscious professionals face a unique challenge: managing multiple online identities without triggering platform bans or compromising personal data. The increasing demand for multi-account management, combined with growing concerns about online privacy and the need for global marketing efforts, has made anti-detect browsers essential business software.
In this guide, we’ll explain what an anti‑detect browser is, how browser fingerprinting works, how anti‑detect browsers counter it, what their core features are, who benefits most from using them, and how to get started with one using BitBrowser as your example tool.
What Is an Anti‑detect Browser
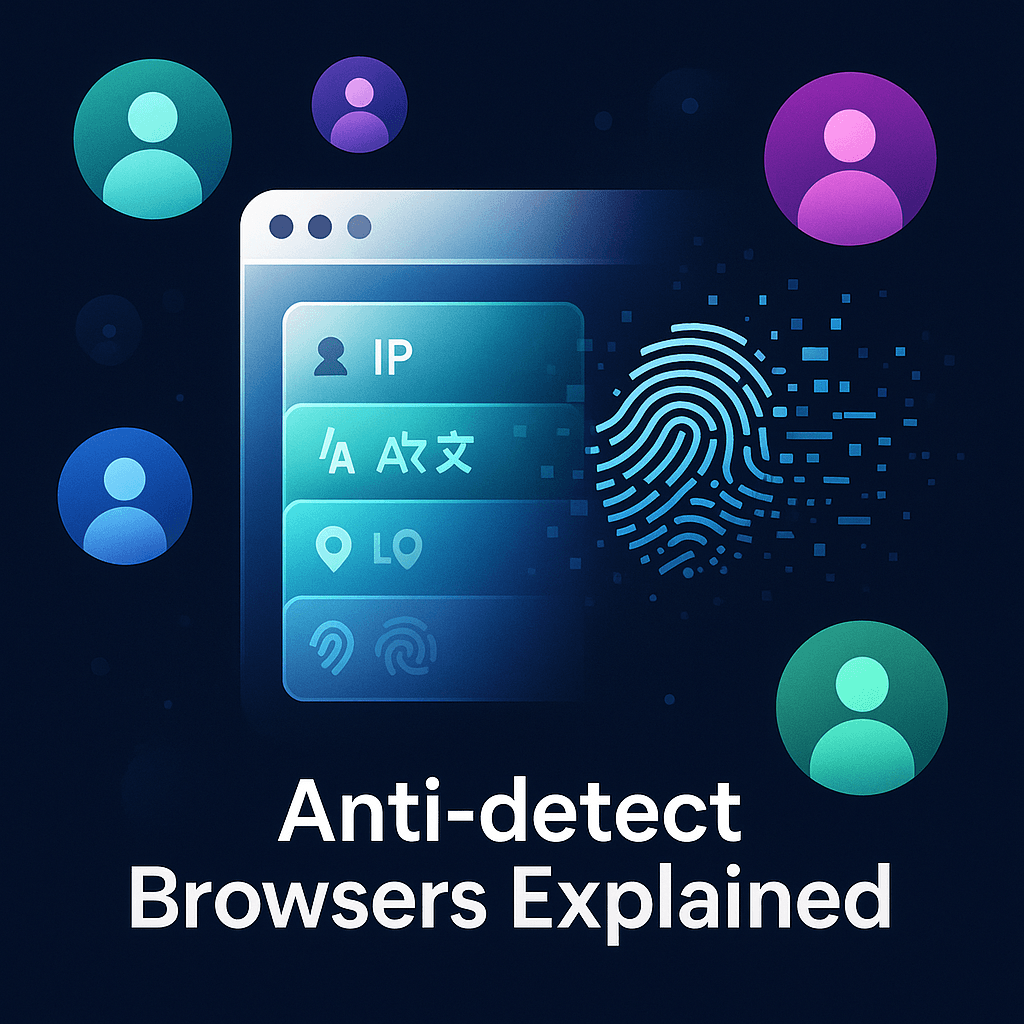
An anti-detect browser is a specialized web browsing application designed to mask, modify, or randomize the unique digital identifiers that websites collect from visitors. Unlike standard browsers such as Chrome, Firefox, or Safari, which transmit consistent device and configuration information with every request, anti-detect browsers actively manipulate these data points to create distinct, isolated browsing profiles that appear as completely separate users to tracking systems.
How Anti-Detect Browsers Work
The core distinction lies in how these tools handle browser fingerprinting, a sophisticated tracking method that extends far beyond simple cookies. When you visit a website, servers automatically gather dozens of technical attributes from your browser and device:
· User agent strings revealing browser type, version, and operating system
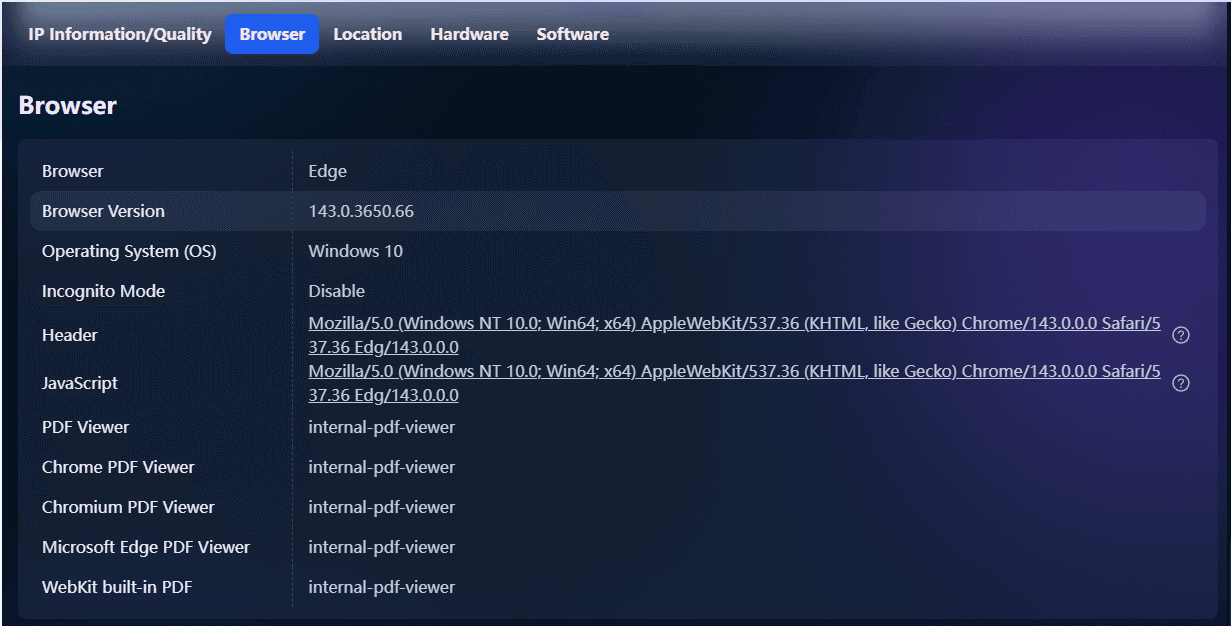
· Screen resolution and color depth specific to your display hardware
· Time zone and language preferences configured in your system
· Installed fonts available for web rendering
· WebGL and Canvas fingerprints generated by how your graphics card renders visual elements
· Audio context fingerprints based on audio processing capabilities
· Installed plugins and extensions that modify browser behavior
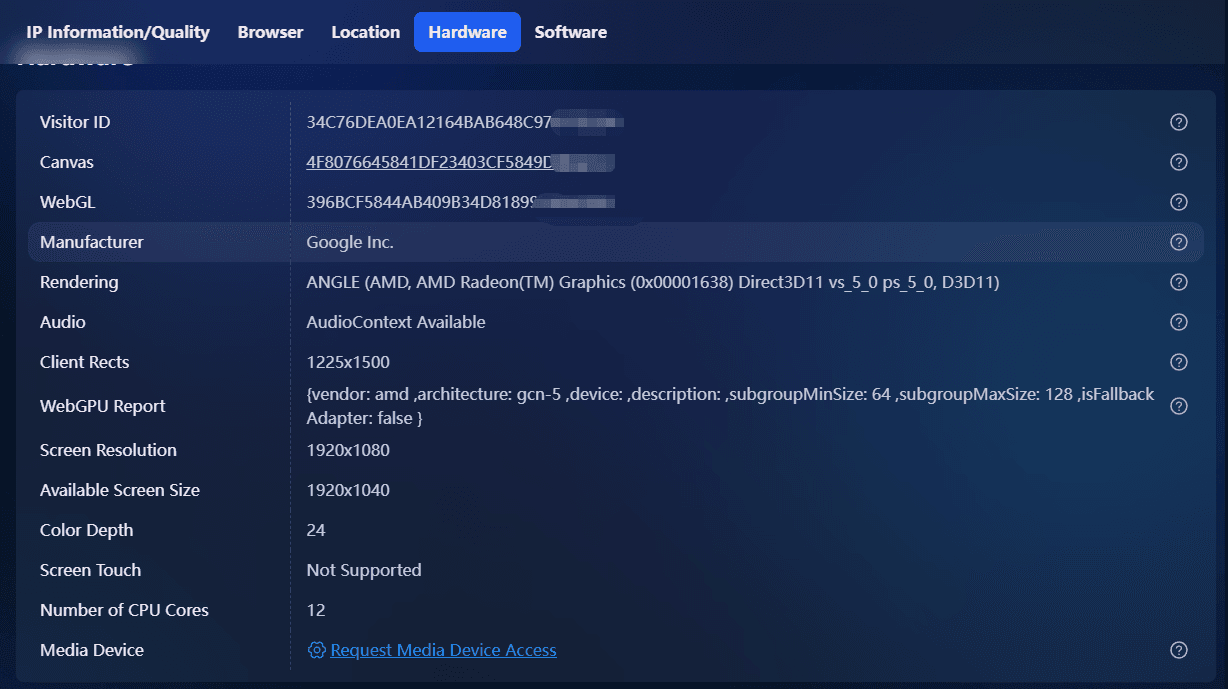
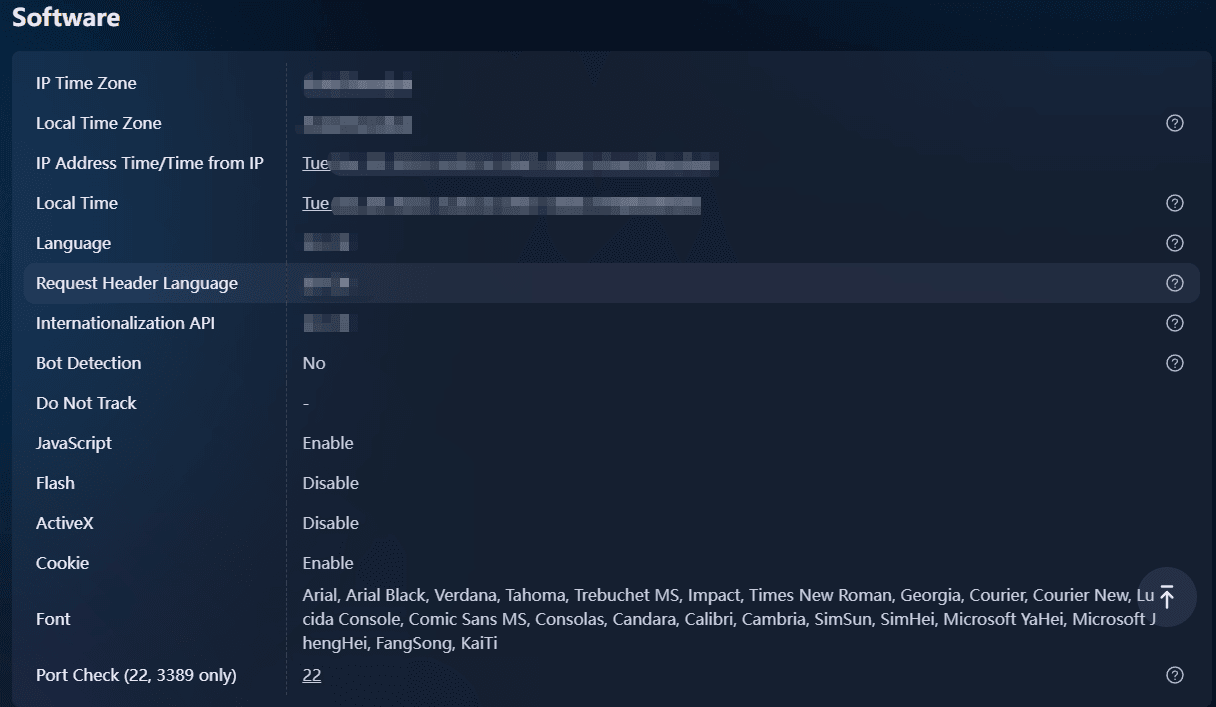
These seemingly innocuous details combine to form a digital fingerprint, a unique identifier as distinctive as a human fingerprint. Research from the Electronic Frontier Foundation demonstrates that browser fingerprints can identify individual users with over 94% accuracy, even when IP addresses change or cookies are cleared.
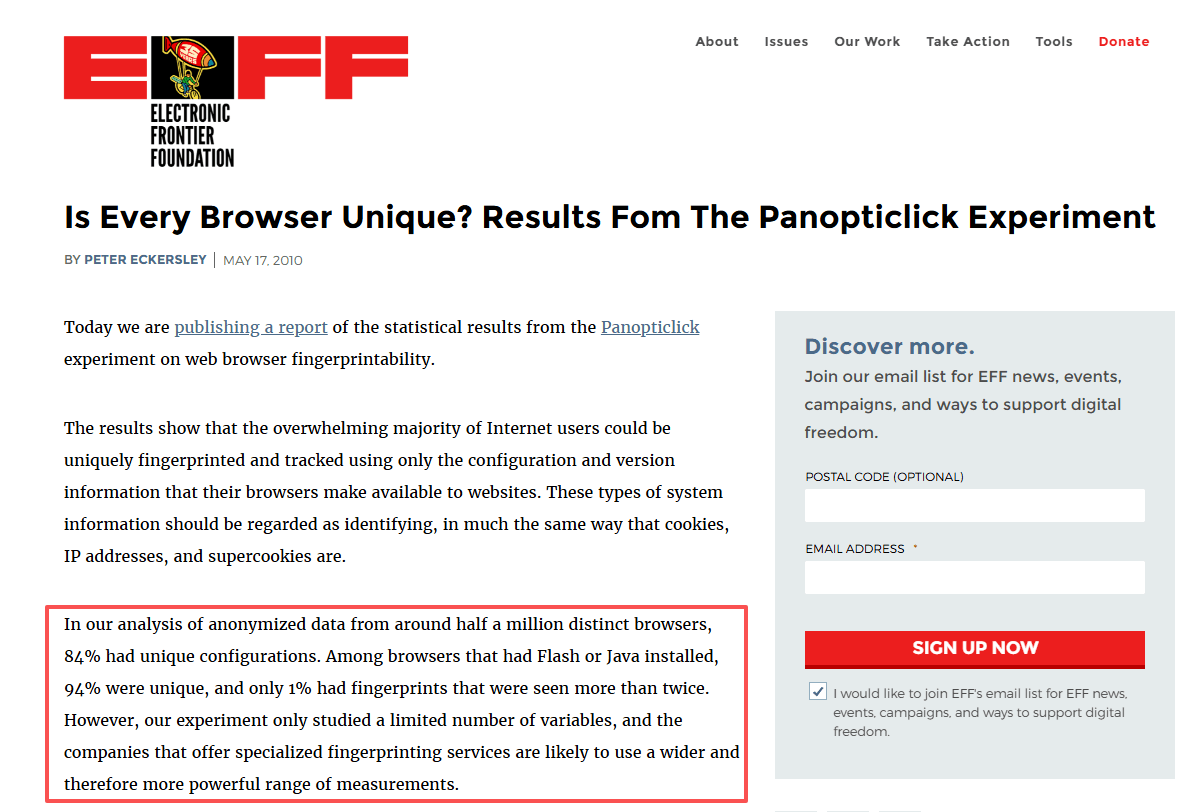
View the Top Browser Fingerprinting Test Tools Compared.
The Purpose of Anti-Detect Browsers
Websites and advertising networks leverage these combined data points to track user behavior across sessions, link multiple accounts to single individuals, and build comprehensive profiles of online activity.
Anti-detect browsers counter this surveillance by generating fresh, randomized fingerprints for each browsing profile, effectively breaking the tracking chain that connects your digital activities. Each profile operates as an independent entity with its own fingerprint signature, preventing platforms from detecting that multiple accounts originate from the same physical device or user.

How Does an Anti-detect Browser Work?
Anti-detect browsers use advanced techniques to hide your digital fingerprint, which is the unique combination of information that websites collect about your device and browser. This technology works by intercepting and changing the data that your browser normally sends to websites.
Creating a New Profile
When you create a new profile in an anti-detect browser, the system generates a complete set of randomized or user-defined browser attributes. This includes modifying the browser's JavaScript environment to return false values when websites ask for identifying information.
For example, if a website wants to know your screen resolution through JavaScript, the anti-detect browser will provide a value that is different from your actual hardware specifications.
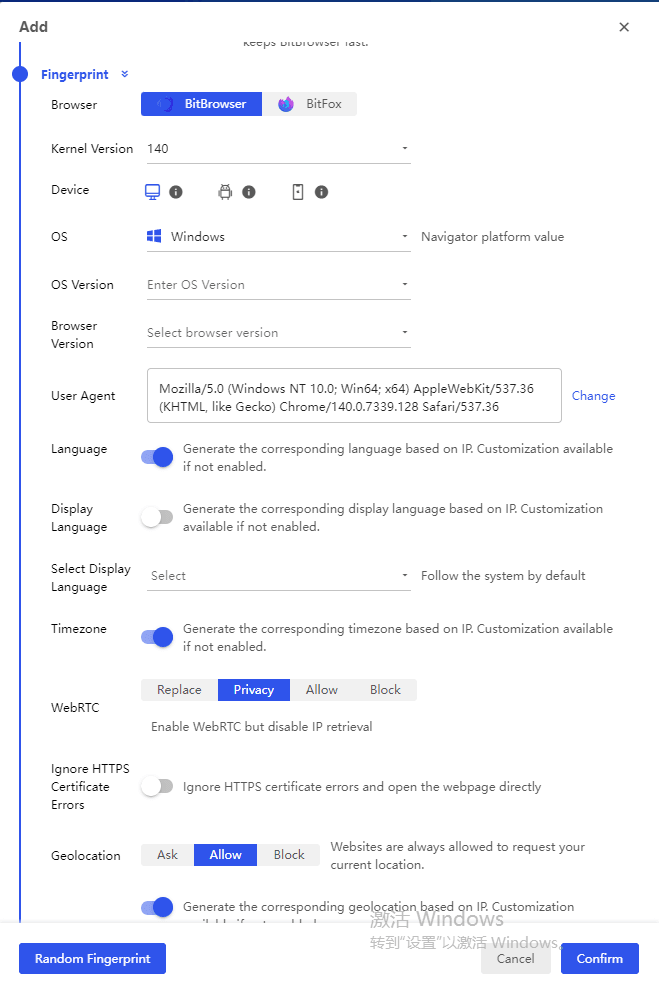
How Anti-Detect Browsers Protect Your Privacy
The internal processes of an anti-detect browser work on multiple levels:
· Canvas fingerprinting protection: The browser adds random noise to HTML5 Canvas rendering, ensuring that the same drawing commands produce slightly different pixel outputs each time. This makes it difficult for websites to track you using canvas-based methods.
· WebGL manipulation: Similar techniques are used for WebGL rendering, where the browser alters GPU-related data to prevent identification based on your graphics hardware.
· Font enumeration blocking: Instead of revealing all the fonts installed on your device, the system presents a carefully chosen list of fonts to websites.
· Timezone and geolocation spoofing: The reported timezone is adjusted to match the location of the proxy IP address being used, creating consistency across all fingerprint elements.

Dynamic Rotation for Added Protection
In addition to these protections, advanced anti-detect browsers also employ dynamic rotation. This means that at predetermined intervals or with each new session, the identifiers being used (such as screen resolution or user agent) are automatically changed. However, care is taken to ensure that these changes still make sense together, avoiding any obvious discrepancies like having a mobile user agent but a desktop screen resolution.
Creating Realistic Fingerprints
The randomization engine in an anti-detect browser uses databases containing real-world device configurations. By doing this, it creates fingerprints that look authentic and blend in with regular internet traffic patterns. This is important because it helps prevent tracking algorithms from connecting different browsing sessions together, even if those algorithms are using advanced machine learning techniques to analyze behavioral patterns alongside technical fingerprints.
Core Features of an Anti-detect Browser
Anti-detect browsers stand out from regular browsers with four main features that work together to create truly separate online identities. These features turn a basic browsing experience into an advanced privacy tool that can handle multiple online personas at the same time.
1. Profile Management
Profile management is the key feature that makes anti-detect browsers work. Each profile acts as its own unique browsing space with its own settings, saved data, and behaviors. Unlike regular browser profiles that share underlying system information, anti-detect browser profiles keep everything separate at the fingerprint level. Users have the ability to create many profiles, each one looking like a different device used by another person. This setup ensures that what happens in one profile stays hidden from tracking systems watching other profiles.
2. IP Address Masking
IP address masking uses proxy servers or VPN connections directly within each browser profile. Instead of sending all internet traffic through one proxy, anti-detect browsers give each profile its own unique IP address, making it seem like there are multiple users in different locations.
For example, someone could use one profile from New York while managing another through a proxy based in London. This setup prevents platforms from realizing that the accounts are operated by the same person. All of this happens directly inside the browser with no need for additional proxy tools.

3. User Agent Spoofing
User-agent spoofing changes the browser’s identifying information so websites think you're using a different device or system. With anti-detect browsers, each profile can pretend to be something else. For example, a Windows computer can appear as macOS Safari.
But changing the user agent alone isn’t enough. Modern websites check many other details, so advanced anti-detect browsers also adjust related fingerprint elements, like screen size, system settings, and hardware details, to match the new user agent. This keeps everything consistent and helps avoid detection.
4. Cookie Management
Cookie management keeps tracking cookies separate within each individual profile, preventing any mixing between accounts. Every profile has its own set of cookies, session storage, and local storage data. This separation stops third-party tracking networks from linking activities across diffe rent profiles using shared cookie identifiers. When someone switches between profiles, the browser loads completely different cookies, making it impossible for websites to connect those sessions through traditional cookie-based tracking techniques.
Use Cases for Anti-detect Browsers
Anti-detect browsers are used in various industries and professional settings where it's crucial to have separate online identities for legitimate business activities. Knowing how these tools are used can help us understand why experts in different fields depend on technology that hides their digital fingerprints.
Multi-Account Social Media Management
Social media managers and agencies handling client portfolios face strict platform policies against operating multiple accounts from a single device. Anti-detect browsers enable professionals to:
· Manage dozens of Reddit, Facebook, or Twitter accounts for different clients without triggering platform security algorithms
· Maintain separate brand identities across LinkedIn profiles for various business ventures
· Operate regional social media accounts for international brands without geographic restrictions
· Prevent account suspensions caused by shared browser fingerprints across business profiles

E-commerce and Marketplace Operations
Online sellers operating across multiple marketplaces require distinct digital footprints to comply with platform rules while maximizing market reach:
· Running separate Amazon, eBay, or Etsy storefronts without cross-contamination of seller metrics
· Testing product listings and pricing strategies across different buyer personas
· Managing inventory across regional marketplaces with geo-specific requirements
· Avoiding account linkage that could result in suspended seller privileges

Digital Advertising Campaign Management
Marketing professionals executing multi-channel advertising campaigns benefit from anti-detect browsers through:
· Creating isolated environments for testing ad creatives across different demographic profiles
· Preventing ad account bans triggered by suspicious login patterns from shared devices
· Collecting unbiased competitive intelligence without personalized search results skewing data
· Managing client advertising accounts across Google Ads, Facebook Ads Manager, and TikTok Ads platforms with distinct authentication credentials
According to Statista, global advertising spending is estimated to reach approximately US$1.16 trillion by 2025, with agencies managing an average of 15-20 concurrent client campaigns requiring separate access protocols.
Is an Anti-detect Browser Illegal?
The short answer: No. Anti-detect browsers are legal software tools in most countries. They function like regular web browsers but offer enhanced privacy and identity protection features. Simply using these tools to safeguard your online presence does not break any laws.
Key legal considerations include:
· Terms of Service (ToS) violations: Using an anti-detect browser to bypass platform restrictions may breach service agreements. Platforms can suspend or ban accounts even if the activity is not illegal under criminal law.
· Fraud and illegal activity: Any use of these tools for fraud, identity theft, financial crimes, or hacking remains illegal and punishable.
· Jurisdictional differences: Privacy laws vary across countries. For instance, the EU’s GDPR and California’s CCPA impose strict rules on how user data can be tracked or processed.
· Legitimate business use: Companies using anti-detect browsers for market research, competitive analysis, or legitimate automation typically face no legal issues.
The Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF) emphasizes that users have the right to control their online presence and use technologies that enhance privacy. The distinction lies in protecting privacy (legal) versus deceiving platforms for harmful purposes (potentially illegal or subject to civil penalties).
Anti-detect Browser vs VPN: What's the Difference?
The comparison between anti-detect browsers and VPNs highlights two different approaches to online privacy, each serving specific purposes. Understanding these differences helps users choose the right tool for their needs.
How VPNs Work
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) operates at the network level. It encrypts your internet traffic and routes it through remote servers, hiding your real IP address. This creates a secure connection between your device and the internet, making it look like you are browsing from another location. VPNs are effective for bypassing geo-restrictions and protecting data on public Wi-Fi, but they only affect one aspect of your digital identity.

How Anti-Detect Browsers Work
Anti-detect browsers work at the application level, modifying many browser fingerprinting parameters at once. While a VPN changes your location, an anti-detect browser changes your digital identity, making you appear as a different user.
Why This Difference Matters for Multi-Account Management
This distinction is especially important for managing multiple accounts. A VPN alone cannot stop platforms from detecting that multiple accounts come from the same device because the browser fingerprint remains the same. Anti-detect browsers create unique digital identities for each profile, which is essential for managing separate business accounts or performing competitive research without overlap.
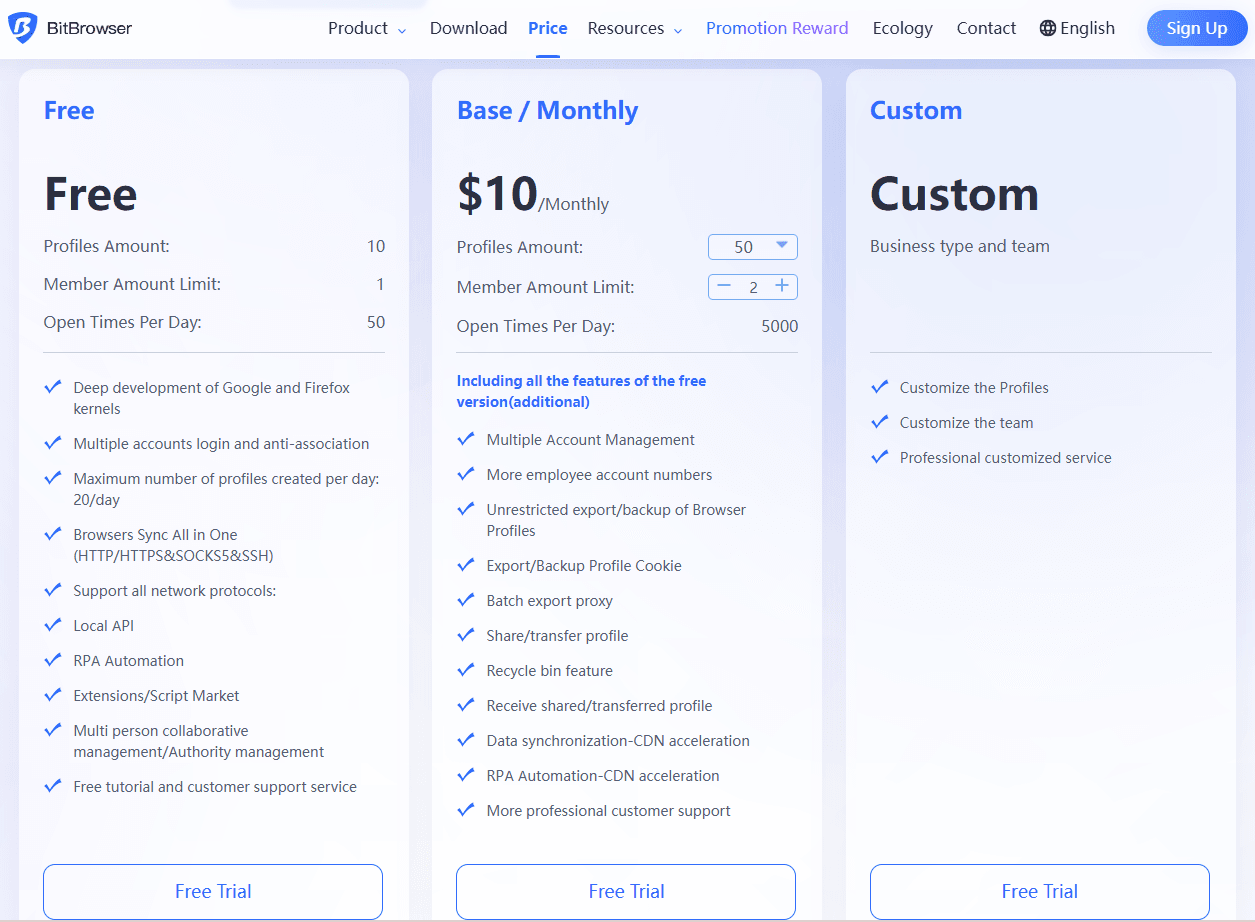
BitBrowser: Beginner-Friendly Multi-account Management
BitBrowser is the beginner-friendly anti-detect browser that combines affordable pricing, comprehensive tools, and the most realistic fingerprint spoofing to keep your profiles secure.
| Core Advantage | Details |
|---|---|
| Affordable Entry Price | Free Forever: 10 browser profiles available for free, zero cost to get started. Low-cost Paid Plans: Affordable plans, starting at $10/month for 50 browser profiles. |
| Comprehensive Features | Batch Operations: Supports batch creation, startup of browser environments, and proxy imports. Team Collaboration: Create sub-accounts, assign permissions for team sharing and auditing. Automation & Extension: Built-in RPA automation tool for repetitive tasks, plus support for various plugins. |
| Realistic Fingerprint Simulation | Comprehensive Simulation: Simulates over 20 browser fingerprint parameters, such as timezone, language, font, Canvas, WebGL, etc., covering both software and hardware features. Smart Coordination: Automatically matches geo-location, timezone, and language parameters when importing proxy IPs, ensuring realistic and trustworthy environments. Detailed Simulation: Can even simulate human-like typing ("human input" mode) to avoid detection by platforms. |
Suggestions for Use and Selection
Start with the Free Plan: It is highly recommended for all beginners to begin with the free plan (10 profiles). This is sufficient to test the tool. Consider upgrading only when you need more profiles or team features.
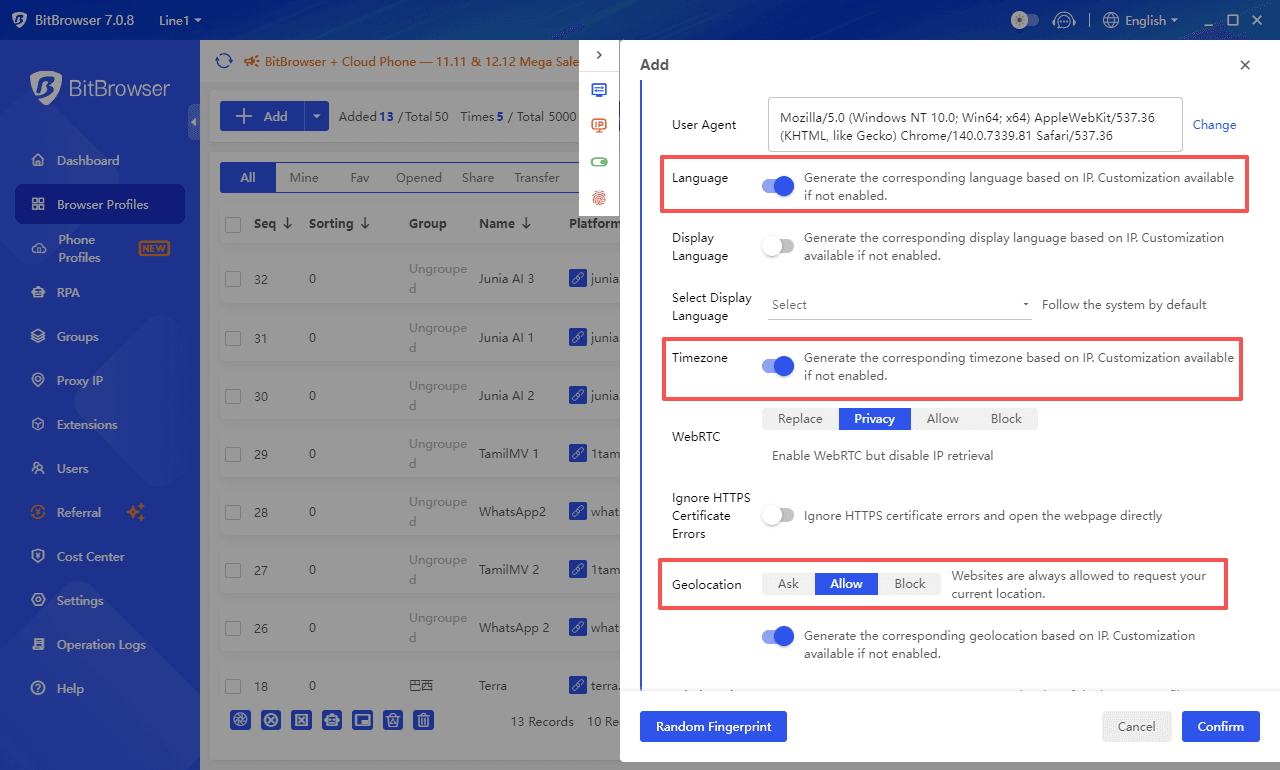
Prioritize Fingerprint Consistency: For beginners, using the "IP-Fingerprint Auto-Match" feature is the safest and most efficient way to ensure a realistic profile. Manually tweaking unfamiliar parameters might inadvertently create detectable anomalies.
Making good use of the official tutorials is key to a quick start.
Conclusion
In the age of heightened online privacy concerns and growing multi-account management needs, anti-detect browsers have become indispensable tools for professionals in various industries. By masking digital fingerprints, they enable users to maintain multiple, distinct online identities without the risk of detection. Whether you're managing social media profiles, e-commerce stores, or digital advertising campaigns, an anti-detect browser like BitBrowser provides the necessary features to keep your activities separate, secure, and undetectable.
FAQ
What is an anti-detect browser?
An anti-detect browser is a specialized tool designed to hide or randomize your digital fingerprint (such as browser type, IP address, screen resolution, etc.) to prevent websites from tracking or identifying you across sessions.
Are anti-detect browsers legal to use?
Yes, anti-detect browsers are legal in most countries. However, using them to violate platform terms of service or engage in fraudulent activities could lead to account suspensions or legal issues.
How does an anti-detect browser differ from a VPN?
While a VPN changes your IP address to hide your location, an anti-detect browser alters your entire digital fingerprint, creating unique identities for each profile. This is crucial for managing multiple accounts without detection.
Can I use BitBrowser for free?
Yes, BitBrowser offers a free tier with 10 browser profiles to get started, making it ideal for beginners. Paid plans are available for users who need more profiles or advanced features.
Why do I need to use an anti-detect browser for multi-account management?
Anti-detect browsers prevent platforms from linking multiple accounts to the same user by altering digital fingerprints, thus avoiding detection and account bans that can occur when using the same device or IP address for multiple accounts.
 YT.Shi
YT.Shi
 Multi-Account Management
Multi-Account Management Prevent Account Association
Prevent Account Association Multi-Employee Management
Multi-Employee Management